UDP Port Scan
Ports tested in the quick UDP scan are DNS 53, TFTP 69, NTP 123, SNMP 161, mDNS 5353, UPNP 1900 and Memcached 11211.
With a valid membership play at the next level on our full featured Online Nmap Port Scanner.
Common UDP Services
| 53 | DNS | The Domain Name System is one of the most common UDP services. It matches host names with IP addresses. DNS is a core part of the Internets plumbing. |
| 123 | NTP | Network Time Protocol allows computers on the Internet to keep time. For computers to work together it helps if they can keep accurate time. |
| 161 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol is a monitoring and configuration protocol, commonly used to monitor system performance and interface utilization. SNMP can be a serious security vulnerability if not managed correctly. |
| 5353 | mDNS | Multicast Domain Name System, this protocol is an implementation of DNS for use on local networks. It uses multicast to resolve host names to IP addresses when there is no configured DNS server. Not something you would expect to see listening on the Internet. |
| 1900 | UPNP | Universal Plug and Play, is a network protocol that was designed for residential and small networks to allow devices such as printers, data sharing and entertainment devices to communicate with each other. Also, not something you would expect to see listening on Internet facing systems. |
Understanding UDP Port Scans
Since UDP is a connectionless protocol, finding open ports is more difficult than testing TCP ports where you are able to get a three-way TCP handshake to confirm the port is open.
In a UDP port scan, there can be some ambiguity in the results. A non-responding port could be a port that is firewalled, or it could be a service that has not recognized the initial packet so did not respond. The other option is a closed port responds with an ICMP Port Unreachable message, this indicates that there is no service running on that port, however, even these can be a little unreliable as a firewall may rate limit or block the ICMP port unreachable messages.
Other ICMP Port Unreachable responses can indicate that a firewall is present, so as you can see UDP Port Scans can be fun.
See the Wireshark examples below for more of an understanding.
ICMP port unreachable messages by the operating system Nmap scans of all 65535 ports can take around 18 hours.UDP Reflection Attacks and Security Implications
UDP port scans should not be ignored by testers as they can leave an organization vulnerable to a number of different attacks, these include exploitable services that can lead to remote execution, or commonly UDP reflection attacks against services such as NTP and DNS. Understanding what services are open through the firewall is an important part of a security vulnerability assessment.
Being a connectionless protocol UDP does not validate the source IP address. An attacker can spoof the IP packet to include any source IP address. By forging the source IP address and sending many packets to multiple UDP servers an attacker is performing a Distributed Denial of Service (DDOS). The amplification factor depends on the protocol. DNS and NTP have been common amplification attack protocols in the past but more recently a much more devastating amplification attack was discovered using Memcached (udp port 11211).
Using memcahced attackers were able to get an amplification factor of 10000 to 50000 times the payload. More details of the amplification vectors and ports can be found on the US Cert Advisory.
UDP Port Scan Samples
In order to understand the responses from a UDP port scan I have scanned my local router with telnet. The scans and responses have been captured with Wireshark in order to display the UDP traffic. The captures were taken on the local host that was running the Nmap scans.
Scan of Port 53
There is no DNS server running on my router, the port is filtered by the local firewall.
Starting Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-03-31 12:17 AEDT Nmap scan report for gateway (192.168.1.1) Host is up (0.00030s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 53/udp open|filtered domain MAC Address: 34:xx:F6:xx:A7:C8 (Unknown)
You can see the open|filtered result in Nmap. This is due to the firewall on the router dropping the UDP packet. No response can be seen in the capture.

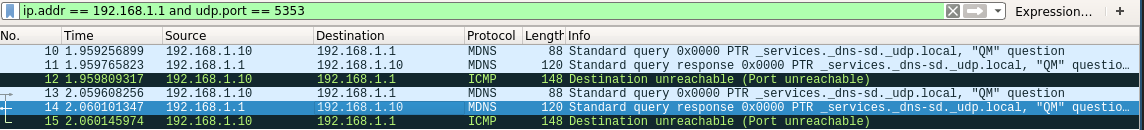
Scan of Port 5353
Multicast DNS is running on the router, as you can see in the Nmap result showing an open port.
Starting Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-03-31 12:18 AEDT
Nmap scan report for gateway (192.168.1.1)
Host is up (0.00036s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
5353/udp open zeroconf
MAC Address: 34:xx:F6:xx:A7:C8 (Unknown)
Response
In the capture you can see the response from the router answering, this comes back to the localhost on a source port of 5353. The localhost does not expect that response so generates an ICMP Port unreachable back to the router.
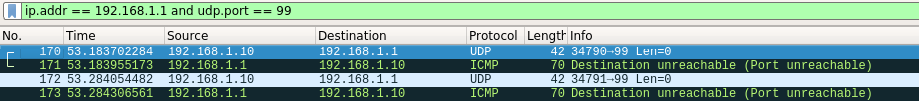
Scan of Port 99
Picking a random port on the router that was not being filtered (UDP port 99) for testing purposes, you can see the router responds with an ICMP Port Unreachable, which Nmap interprets as a closed port.
Starting Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-03-31 12:23 AEDT
Nmap scan report for gateway (192.168.1.1)
Host is up (0.00024s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
99/udp closed metagram
MAC Address: 34:xx:F6:xx:A7:C8 (Unknown)
Response
In this test the Wireshark capture shows the scan and the ICMP response that indicates a closed port.
Assess the risk and work on mitigation.
Remove limits with a full membership.
Next level testing with advanced Security Vulnerability Scanners.
Trusted tools. Hosted for easy access.